Deconvolution Anlaysis
Overview
The goal of this analysis is to apply deconvolutional model to identify cell type-specific differentially expressed genes (csDEGs). In this project, we have both flow cytometry and gene expression data on the same samples. The deconvolutional model will be built on the bulk RNA-seq data with known cell proportions estimated from the flow cytometry data.
With flow cytometry data, we can identify proportions of different cell populations from the whole blood samples. Identification of cell populations and estimation of corresponding cell proportions are done using the DAFi approach we recently developed. DAFi is an automated gating strategy that can effectively reduce human bias in the subjective manual gating analysis.
The deconvolutional model, dubbed as “FastMix”, is a new analytic pipeline co-developed by our team, that combines the deconvolution step with downstream analysis based on linear mixed-effects regression model. It takes gene expression data, cell proportions, and demographic covariates as input, and fits a linear mixed-effects model using a novel computationally-efficient moment-based covariance estimator, which is robust and can achieve comparable accuracy with the traditional EM-based mixed-effects model fitting algorithm. Based on the deconvolutional model, the analytical pipeline also provides a novel comptetitive hypothesis test to identify genes that have significantly larger or smaller predicted random effect (cell type-specific expression) with a given covariate, a.k.a. csDEGs. To learn more about FastMix, please read here.
This report is organized in the following sections.
- Cell proprotions and demographic covariates. Detailed view of the data to be used in the model. Note that the within-subject correlation is not negligble.
- Model fitting. Fit the FastMix model: \[\mbox{gene expression ~ cell proportions + response after dose 2 + age}.\]
- Downstream analyses:
- Identification of cell type-specific markers. Neutrophil markers are identified as the fixed effect inference from the deconvolutional model.
- Validation with scRNA-seq markers. The above neutrophil markers derived from the deconvolutional model are validated with the neutrophil markers derived from an independent single cell RNA-seq data analysis on the same subjects. A significant amount of commonly identified marker genes are reported.
- csDEGs and pathway analysis. csDEGs are identified from the novel hypothesis test on the random effect predictions, and pathway enrichment analysis is performed on the top csDEGs to understand their biological functions using ReactomePA.
- Discriminant score. A discriminant score on cross-validation datasets shows that age is an impacting factor for vaccine response.
Load useful packages.
library(FastMix)
library(ReactomePA)Cell proportions and demographic covariates
Cell proportions
We load cell proportions from the file “HVP_CD66CD45Subsets.csv” to cellprop.
cellprop <- read.csv("../HVP_CD66CD45Subsets.csv", row.names = 1)For this deconvolution analysis, we work with three abundant cell populations:
- the CD66 positive and CD45 positive (CD66pCD45p) population - this is the neutrophil cell type,
- the CD66 negative and CD45 positive (CD66nCD45p) population, and
- the rest population - for all other cells.
The average proportions for the above cell populations are 0.219, 0.136, 0.645, respectively. Cell proportions sum up to 1.
Demographic covariates
We consider two demographic covariates: response after dose 2 and age. From the sample table , we curate and store those covariates in demo.
demo <- ctab %>% column_to_rownames(var="Sample_name") %>% dplyr::select(Responder_dose2, Age)
demo$Responder_dose2 <- as.numeric(demo$Responder_dose2)All covariates
The following figures show detailed overview of cell proportions and demographic covariates. 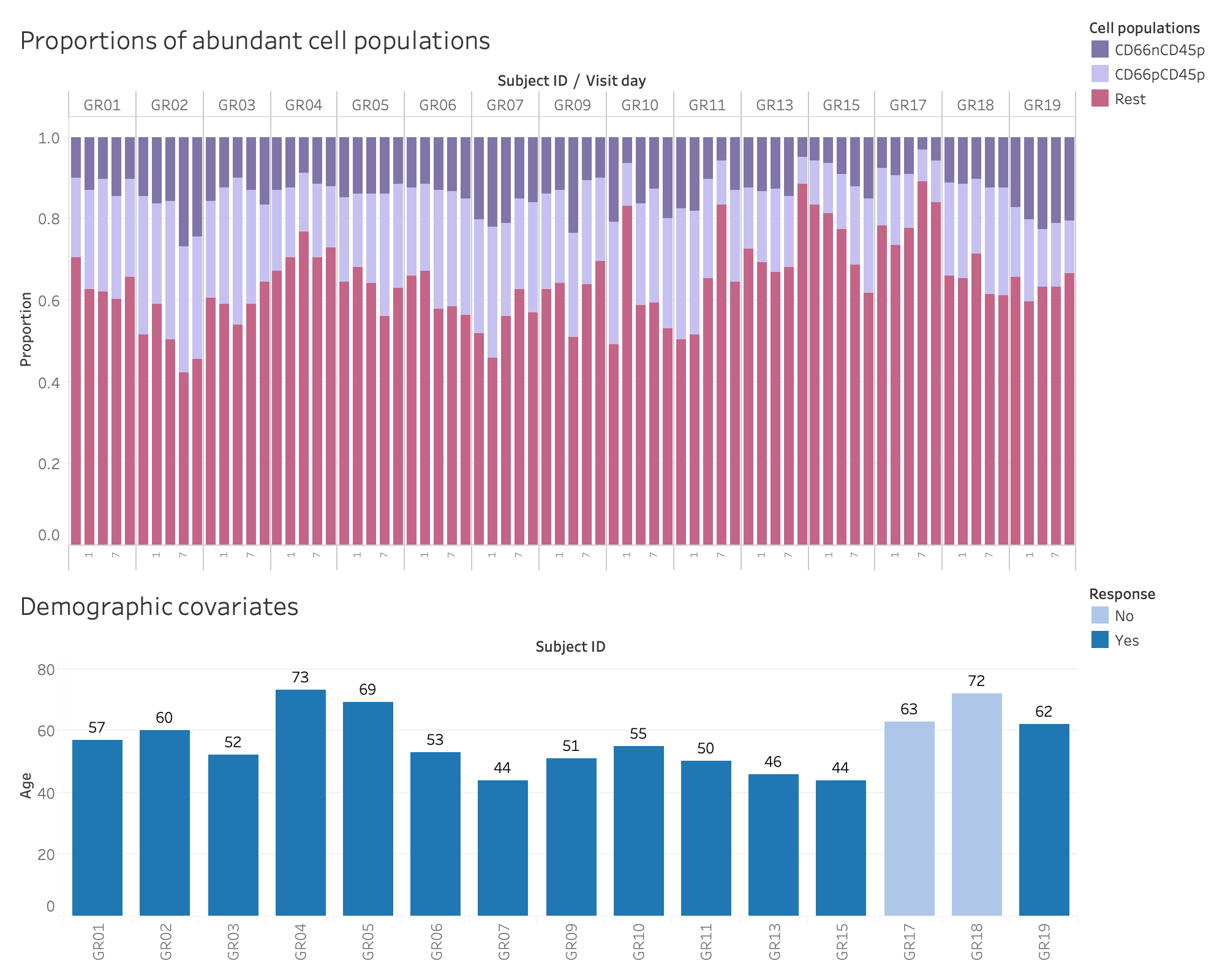
Within-subject correlation
To make the best use of the multiple time points data, we use PBtest again to estimate the within-subject correlation, which will be provided to the weighted FastMix model for handling repeated measurements.
cov_matrix <- PBtest::getSigma(t(dat.filt10.symbol), ctab$Responder_dose2, ctab$Subject_id)
(rhohat <- cov_matrix[2])## [1] 0.3789871Note that there is quite strong correlation (= 0.379) within-subject, ignoring which is not recommended.
Model fitting
Recall that our deconvolutional model is a regression-like model associating the bulk gene expression level with the covariates. \[\mbox{gene expression ~ cell proportions + response after dose 2 + age}\]
Using cellprop, demo, and cov_matrix obtained above, we fit the deconvolution model for the bulk RNA-seq data dat.filt10.symbol as follows.
set.seed(1234)
mod <- FastMix(GeneExp=dat.filt10.symbol, CellProp=cellprop, Demo=demo,
independent=F, include.demo=FALSE, cov_matrix=cov_matrix)
round(mod$fixed.results, 4)## betahat tstat p.value p.adj
## CD66pCD45p 6.9217 216.2982 0.0000 0.0000
## CD66nCD45p 7.4261 277.9615 0.0000 0.0000
## rest 7.1561 257.7759 0.0000 0.0000
## CD66pCD45p.Responder_dose2 -0.0006 -0.0540 0.9571 0.9622
## CD66nCD45p.Responder_dose2 0.0548 2.7021 0.0088 0.0132
## rest.Responder_dose2 0.0010 0.7372 0.4636 0.5961
## CD66pCD45p.Age 0.0560 6.7510 0.0000 0.0000
## CD66nCD45p.Age 0.0006 0.0476 0.9622 0.9622
## rest.Age -0.0169 -12.8567 0.0000 0.0000colSums(mod$re.ind.pvalue < 0.05)## CD66pCD45p CD66nCD45p
## 691 146
## rest CD66pCD45p.Responder_dose2
## 266 203
## CD66nCD45p.Responder_dose2 rest.Responder_dose2
## 113 1624
## CD66pCD45p.Age CD66nCD45p.Age
## 261 274
## rest.Age
## 890The above are number of cell type-specific markers (CD66pCD45p, CD66nCD45p, rest) and csDEGs for each interaction terms (CD66pCD45p.Responder_dose2, CD66nCD45p.Responder_dose2, rest.Responder_dose2, CD66pCD45p.Age, CD66nCD45p.Age, rest.Age).
Downstream analyses
We use the following chunk to perform downstream analyses all at one pass.
Ntop <- 100
## map gene symbols to entrez ids
library(org.Hs.eg.db)
map2entrez <- mapIds(org.Hs.eg.db, rownames(dat.filt10.symbol), 'ENTREZID', 'SYMBOL')
## pathway analysis for each random-effect/cell-type-specific DEG list
covariates <- rownames(mod$fixed.results)
lst.top.DEG <- lst.sig.path <- vector("list", length=length(covariates))
names(lst.top.DEG) <- names(lst.sig.path) <- covariates
for(term in covariates){
# cat(term, "\n")
top.genes <- names(sort(mod$re.ind.pvalue[,term])[1:Ntop])
sig.path <- enrichPathway(gene=map2entrez[top.genes], pvalueCutoff=0.05, readable=T)
lst.sig.path[[term]] <- sig.path
lst.top.DEG[[term]] <- top.genes
}
## top DEGs
tab.top.DEG <- do.call("cbind", lst.top.DEG)Identification of cell type-specific markers
For now, let’s focus on the top 100 markers or csDEGs from the deconvolutional model. Table below is ordered in increasing p-values (most siginificant to least significant) column-wise.
## top DEGs
kable(tab.top.DEG) %>%
add_header_above(c("Cell type-specific markers" = 3, "csDEGs" = 6)) %>%
kable_styling() %>%
scroll_box(width = "100%", height = "500px")| CD66pCD45p | CD66nCD45p | rest | CD66pCD45p.Responder_dose2 | CD66nCD45p.Responder_dose2 | rest.Responder_dose2 | CD66pCD45p.Age | CD66nCD45p.Age | rest.Age |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RSAD2 | RSAD2 | HLA-V | ZNF774 | ZNF774 | TCL1A | RSAD2 | RSAD2 | TMEM176A |
| IFITM3 | BATF2 | USP18 | RSAD2 | HLA-L | OAS3 | IFI44L | CD177 | KDM5D |
| FCGR3B | SERPING1 | KDM5D | RPS4Y1 | CYP4F29P | RSAD2 | GSTM1 | BATF2 | DDX3Y |
| ACSL1 | ETV7 | XIST | IFI44L | JUP | OASL | TMEM176B | SERPING1 | PRKY |
| IFIT1 | USP18 | RPSAP58 | IFIT1 | KREMEN1 | IFI44L | IFIT1 | ISG15 | TMEM176B |
| IFIT2 | ANKRD22 | PRKY | XIST | RSAD2 | HERC5 | SERPING1 | ZNF774 | USP9Y |
| AQP9 | IFIT1 | C4BPA | DDX3Y | RP11-20D14.6 | MX1 | TMEM176A | IFIT1 | RPS4Y1 |
| IFIT3 | ATF3 | RPS4Y1 | KDM5D | BATF2 | JUP | HLA-L | RPL34 | TXLNGY |
| BASP1 | ISG15 | DDX3Y | SERPING1 | IFITM3 | USP18 | IFIT3 | ETV7 | GSTM1 |
| CXCR2 | IFI44L | UTY | ISG15 | SERPING1 | IFIT1 | HERC5 | HERC5 | FADS2 |
| IFITM2 | RPS27 | RSAD2 | HERC5 | RAP1GAP | ISG15 | ZNF774 | USP18 | DAAM2 |
| CXCR1 | NRIR | RPL13P12 | PRKY | ETV7 | ZNF774 | RPS4Y1 | MX1 | UTY |
| MME | SEPT4 | RPS4X | USP18 | GATA2 | IGLV3-21 | XIST | MT2A | ZNF774 |
| DYSF | MALAT1 | RP11-20D14.6 | IFIT3 | ANKRD20A11P | IGLC3 | ISG15 | RPL31 | CD177 |
| PROK2 | RPL34 | USP9Y | TXLNGY | RUNDC3A | IGHA2 | USP18 | IFIT3 | TRDV2 |
| HERC5 | CD177 | MIR3945HG | RP11-20D14.6 | IGLV3-21 | IGHA1 | OAS3 | IFI6 | CYP4F29P |
| NAMPT | EXOC3L1 | LAMP3 | OASL | HDC | IGHD | IFI44 | TNFAIP6 | XIST |
| MX1 | HERC5 | OTX1 | CYP4F29P | RPL34 | ANKRD20A11P | CMPK2 | IFITM3 | SC22CB-1E7.1 |
| MMP9 | RP11-476D10.1 | TXLNGY | MX1 | GZMK | CYP4F29P | CD274 | IFI44L | RP11-20D14.6 |
| IL1RN | RPL31 | TGM3 | OAS3 | PAX8-AS1 | HLA-DQA2 | BATF2 | KREMEN1 | CATIP |
| KCNJ15 | FCGR1A | ZNF774 | EIF1AY | HLA-G | IGLV1-40 | IFIT2 | RPL23 | UTS2 |
| CSF3R | CMPK2 | ANXA3 | LAMP3 | CD177 | IGHV3-23 | OASL | ANKRD22 | HLA-L |
| MNDA | RPL23 | LYZ | EIF2AK2 | IFIT1 | EIF2AK2 | DDX3Y | CMPK2 | DGKK |
| MGAM | HLA-L | HLA-DQB1 | BATF2 | SECTM1 | APOBEC3A | PRKY | GZMK | XRRA1 |
| ISG15 | HLA-G | HLA-DRB5 | IFIT2 | HBM | IGHV4-39 | KDM5D | OASL | ANKRD36BP2 |
| TNFRSF10C | C1QB | RP4-568C11.4 | USP9Y | ISG15 | CD22 | IFI6 | IFIT2 | TPST1 |
| IFI44L | RAP1GAP | ACTBP8 | CMPK2 | ADM | IGLC2 | FCGR1A | DAAM2 | EIF1AY |
| FPR1 | FCGR1CP | UBB | IFI6 | RPL31 | PAX8-AS1 | APOBEC3B | OAS3 | ZFY |
| FFAR2 | DOCK4 | EEF1A1 | IL1RN | FCGR1A | IGKC | FCGR1B | RPS3A | AC007278.3 |
| SOD2 | EEF1A1 | LINC01410 | FAM118A | HLA-H | RP11-20D14.6 | FADS2 | OAS1 | HLA-DRB5 |
| FCGR2A | TNFAIP6 | PRDM5 | ANKRD20A11P | SLC45A3 | CD8A | HLA-DQA2 | ATF3 | BCAT1 |
| ALPL | TPT1 | OR52K3P | SIGLEC1 | RPH3A | IFI44 | IFITM3 | PDK4 | ACCS |
| SELL | LAMP3 | TNFAIP6 | IGLC3 | SPTB | LAMP3 | LAMP3 | RPS27 | RAVER2 |
| MX2 | RPS3A | TTC26 | IGLV3-21 | KLF1 | SIGLEC1 | NECTIN2 | RPS24 | APOBEC3B |
| LITAF | CD274 | RP11-326C3.15 | IFI44 | IFIT3 | OLFM4 | HLA-G | RPS7 | LTF |
| BCL6 | GATA2 | GYPC | CD274 | MT2A | FCRL1 | EPSTI1 | CYP4F29P | SLC1A7 |
| OAS3 | FCGR1B | CTC-490G23.2 | DDX58 | TMPRSS9 | IGHV1-18 | FFAR2 | RPL26 | LILRB5 |
| MXD1 | CASP5 | RP11-326C3.12 | UTY | IGHA2 | SC22CB-1E7.1 | CASP5 | AC007278.3 | FGFBP2 |
| LRRK2 | AHNAK | IFIT1 | PADI2 | HERC5 | IGHV1-3 | HLA-J | LILRA5 | DDX11 |
| MMP25 | HLA-W | EEF2 | ANKRD22 | ANKRD22 | IFI6 | DOCK4 | DDX58 | RAP1GAP |
| FPR2 | RPS24 | SLC25A39 | TNFAIP6 | RPL23 | RP11-164H13.1 | GBP5 | LRG1 | PRSS23 |
| FAM129A | RP11-531H8.2 | BTNL3 | TMPRSS9 | HLA-W | JCHAIN | JUP | RPL9 | SAPCD2 |
| STEAP4 | RPL9 | BMX | SAMD9L | FCGR1B | TCL6 | IL1RN | SECTM1 | CRISP3 |
| VNN2 | KREMEN1 | CD177 | SC22CB-1E7.1 | SELENBP1 | HLA-DRB5 | KCNJ2 | IFI35 | KIR2DS4 |
| CSF2RB | C1QA | RP11-875O11.3 | UTS2 | SLC6A8 | RPS4Y1 | PLSCR1 | RPS17 | LRRN3 |
| APOBEC3A | RPS6 | ZFY | EPSTI1 | IGHA1 | ERAP2 | RPL31 | STX11 | GZMH |
| DDX60L | MSR1 | FAM157B | LGALSL | IGKV1-6 | FCER2 | ADM | CRISPLD2 | SPON2 |
| RNF24 | MT2A | RPS12 | NTNG2 | ATF3 | HLA-L | GBP1 | IDO1 | FAM118A |
| ITM2B | CACNA1E | B3GNT5 | CASP5 | RPL26 | HLA-DRB6 | HCAR2 | IL1RN | TACSTD2 |
| KRT23 | HDC | HERC5 | DDX60 | TAL1 | XIST | GZMH | SEPT4 | PODN |
| HLA-C | RPS7 | TMSB4X | DDX60L | IFIT2 | FAM129C | ITGA1 | PGLYRP1 | ADGRG1 |
| IFI6 | ZNF774 | ST3GAL4-AS1 | PLSCR1 | NAMPTP1 | ESPN | SIGLEC1 | FBXO6 | MYOM2 |
| LIMK2 | RPH3A | HIST2H2BF | RUNDC3A | TNFAIP6 | TNFRSF13C | PROK2 | EXOC3L1 | JUP |
| LYN | RPS18 | IFI44L | IFIT5 | IFI6 | SNX22 | AOC1 | EEF1B2 | NT5M |
| SERPING1 | SIGLEC1 | TMTC1 | KCNJ15 | LRG1 | CD8B | USP9Y | WARS | NT5E |
| SLC2A3 | RPS17 | CXCL1 | HLA-DRB5 | DOCK4 | IGLV1-51 | GATA2 | SIGLEC1 | ZNF683 |
| S100A9 | RPL13A | TBC1D3L | EXOC3L1 | RPS24 | DSC2 | DHRS9 | PHC2 | SERPINB10 |
| C5AR1 | IFI6 | TMSB10 | DSC2 | RPS17 | CA4 | RPL34 | SDC3 | C9orf78 |
| NCF1 | CYP26B1 | RPS27A | CEACAM1 | TMEM140 | IGHV3-21 | TXLNGY | RPH3A | GABPB1-AS1 |
| OASL | RMI2 | PROK2 | DHRS9 | CMPK2 | MYBL2 | TENM1 | CDA | WASH6P |
| ADAR | RPL3 | TNFRSF9 | IFIH1 | VWCE | CMPK2 | XAF1 | C19orf35 | IFI44L |
| SPI1 | LYPD2 | MMP9 | RPL34 | DMTN | DBNDD1 | MX1 | CASP5 | ST14 |
| NTNG2 | RPS27A | GABPB1-AS1 | IGHA2 | CD8A | NBPF26 | ZBP1 | RPL7 | ALAS2 |
| LRG1 | SPATS2L | RPL37 | MMP9 | CPA3 | NTNG2 | EIF2AK2 | FCGR1A | GZMB |
| GCA | IDO1 | DNAJC3-AS1 | ZCCHC2 | SLC4A1 | IGHG1 | SAMD9L | RPL21 | NECTIN2 |
| MSRB1 | FRMD3 | CA4 | TNFSF13B | RPS7 | PAM | UTY | ODF3B | OLFM4 |
| ADGRG3 | B2M | MGAM2 | IGHA1 | CDKN1C | NECTIN2 | KCNJ15 | ASPRV1 | NEBL |
| IGF2R | OASL | CD74 | ZNF117 | RPS27 | GABPB1-AS1 | HCAR3 | NFIL3 | AP001189.4 |
| TNFAIP6 | IGHV4-4 | PLIN4 | HELZ2 | EPB42 | KRT23 | CATIP | TMEM140 | BTN3A2 |
| PHC2 | TRIM9 | FKBP8 | C4BPA | SIPA1L2 | THBD | SCARF1 | CCNJL | IFI27 |
| QPCT | IFIT3 | GPX3 | OR52K3P | DSP | HERC6 | TNFAIP6 | TCN2 | F5 |
| MEGF9 | SCO2 | LINC01094 | RP11-329N15.3 | RPS3A | DEFA3 | DDX11 | SNHG8 | LCN2 |
| SMCHD1 | TTC26 | RPL10 | RPL41 | USP18 | AC104809.4 | SECTM1 | LINC00694 | TRGV9 |
| TNFSF10 | GSTM1 | SPP1 | OR2W3 | SOCS3 | AFDN | NAIP | SIPA1L2 | HP |
| ACTN1 | RPL7 | RP1-34B20.21 | RPL21 | FKBP8 | LTF | IFI27 | TYMP | RP11-678G14.3 |
| NCF1C | DDX11L10 | CLEC4D | RPL13P12 | CD8B | ANKRD36BP2 | RPL23 | RPS15A | FCGR2B |
| S100A11 | SLC45A3 | EXOC3L1 | AGRN | CTC-510F12.4 | IFIT2 | ACCS | DYSF | IFI44 |
| DDX58 | RP11-326C3.15 | NAMPTP1 | OAS2 | GP9 | CNTNAP2 | CEACAM1 | CSRNP1 | ITGA1 |
| RNF149 | SDC3 | RPL13 | RPL31 | CXCR1 | CD72 | ANKRD22 | GOLGA8B | GSTM4 |
| FRAT2 | IL7R | GALNT14 | GABPB1-AS1 | UBXN6 | RAP1GAP | GK | U2AF1L5 | ARRDC4 |
| XPO6 | RPS4Y1 | RP11-332M2.1 | PTGS2 | SLC25A39 | FMN1 | PARP9 | DOCK4 | PDGFRB |
| SECTM1 | SLC6A9 | RPL5 | FAM8A1 | THEMIS | LINC01410 | DDX60L | ADM | CYP1B1 |
| TLR1 | CPA3 | RP11-213H15.1 | AC009506.1 | RILP | CAMP | DDX60 | UBE2L6 | HLA-DRB6 |
| TLR8 | RPS20 | RPL11 | NECTIN2 | ASPRV1 | MACROD2 | CXCR1 | MARCO | ARHGAP24 |
| SERPINA1 | AQP1 | HECW2 | FPR2 | CDKN1A | CD79B | LRG1 | TNFSF13B | CAMP |
| LRP10 | GNLY | LIPN | FFAR2 | ANKRD9 | IGHV3-30 | KRT72 | H3F3AP4 | SDC2 |
| PPP1R3B | EEF1B2 | LRRN1 | RPL23 | IGHV4-4 | CXCR5 | IFI35 | LAP3 | PADI4 |
| EGLN1 | RPL11 | AP1M2 | GBP1 | PDZK1IP1 | MMP9 | XRRA1 | HELZ2 | CTD-2017D11.1 |
| HLA-E | RP11-13A1.1 | RP1-167A14.2 | KIAA1958 | IGKV1-17 | OAS2 | CACNA1E | ACSL1 | PGLYRP1 |
| PLXNC1 | RP11-329N15.3 | RPL3 | PROK2 | TCL1A | LCN2 | SLPI | RPS18 | KIF19 |
| CYP4F3 | AKAP12 | TTTY15 | CA4 | IFI44L | C4BPA | TMEM140 | IL7R | IL7R |
| TMEM140 | RTP4 | ISG15 | RPS27 | GABARAP | IL1RN | KRT73 | SPATS2L | SDK2 |
| MBOAT7 | SLC26A8 | RPL36AL | ZBP1 | ODF3B | DDX60L | UBE2L6 | CD274 | VENTX |
| SORL1 | RP3-508I15.14 | RPLP1 | MX2 | RPL9 | CDKN1C | C1QA | PLSCR1 | GSTM2 |
| KIAA1551 | IFI27 | RPS23 | THBD | TCN2 | LGALSL | HIST1H2BD | LINC01272 | NELL2 |
| NFAM1 | IGF2BP3 | RP11-34P13.13 | HERC6 | MS4A2 | LINC00926 | NTNG2 | FAM26F | RORC |
| TNFSF13B | GCSAML | NACA | JUP | FAM26F | CD79A | KIR2DS4 | FRMD3 | WASH7P |
| HLA-B | U2AF1L5 | USP32P1 | RPL11 | TNS1 | VNN3 | U2AF1 | GBP1 | CTC-490G23.2 |
| NCF2 | LINC00694 | BCORP1 | BASP1 | ADARB2 | IGHM | RNF182 | GP9 | FBLN5 |
| TRIM25 | RPL21 | RPL13A | HCAR2 | AKAP12 | IGKV3-20 | SPATS2L | RP11-476D10.1 | SCART1 |
The first column is the neutrophil markers derived from the deconvolutional model. The top neutrophil markers are RSAD2, IFITM3, FCGR3B, ACSL1, IFIT1, IFIT2.
Validation with scRNA-seq markers
Independently, single immune cell RNA-seq data are analyzed by Brian Aevermann, following the Louvain clustering for cell populations identification and MAST generalized linear model for marker gene identification of the identified cell population clusters. Neutrophils are one of the major cell population clusters identified in the single cell analysis. The single cell analysis identified 365 markers for the neutrophils, which is available upon request.
We overlay the two marker genes list in the following venn diagram. A hypergeometric test shows the overlapping of the venn diagram is highly significant.
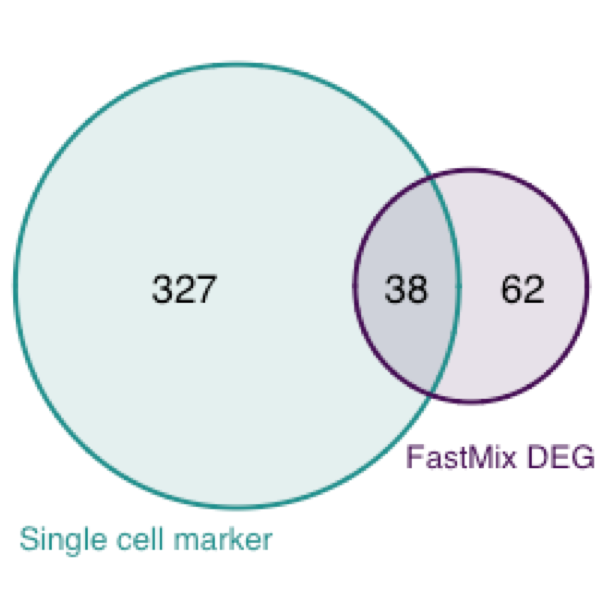
## hypergeometric test
phyper(38,365,13157-365,100, lower.tail=FALSE)## [1] 4.969543e-35The common marker genes are
## read in the common marker genes from a pre-saved file
commongenes <- read.csv("../tab_commongenes_singlecell_comparison_top100.csv", col.names = "Marker gene")
commongenes## Marker.gene
## 1 IFITM3
## 2 FCGR3B
## 3 ACSL1
## 4 IFIT2
## 5 AQP9
## 6 BASP1
## 7 CXCR2
## 8 IFITM2
## 9 CXCR1
## 10 PROK2
## 11 NAMPT
## 12 CSF3R
## 13 MNDA
## 14 TNFRSF10C
## 15 FPR1
## 16 FFAR2
## 17 SOD2
## 18 FCGR2A
## 19 LITAF
## 20 MXD1
## 21 VNN2
## 22 APOBEC3A
## 23 ITM2B
## 24 HLA-C
## 25 LYN
## 26 S100A9
## 27 C5AR1
## 28 NCF1
## 29 GCA
## 30 MSRB1
## 31 NCF1C
## 32 S100A11
## 33 RNF149
## 34 FRAT2
## 35 TLR1
## 36 MBOAT7
## 37 SORL1
## 38 NCF2csDEGs and pathway analysis
Also we looked at the top 100 csDEGs for each interaction term. Based on these csDEGs, we performed pathway analysis using the Reactome pathways and ReactomePA Bioconductor package.
Below are significant pathways identified for the interaction term with the response covariate after dose 2. We see that the interferon immune signaling related pathways are frequently picked up.
## significant pathways
lapply(lst.sig.path[4:6], function(z) z$Description)## $CD66pCD45p.Responder_dose2
## [1] "Interferon Signaling"
## [2] "Interferon alpha/beta signaling"
## [3] "Antiviral mechanism by IFN-stimulated genes"
## [4] "ISG15 antiviral mechanism"
## [5] "Influenza Infection"
## [6] "Peptide chain elongation"
## [7] "Viral mRNA Translation"
## [8] "Eukaryotic Translation Elongation"
## [9] "Selenocysteine synthesis"
## [10] "Eukaryotic Translation Termination"
## [11] "Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD) independent of the Exon Junction Complex (EJC)"
## [12] "Formation of a pool of free 40S subunits"
## [13] "L13a-mediated translational silencing of Ceruloplasmin expression"
## [14] "SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane"
## [15] "GTP hydrolysis and joining of the 60S ribosomal subunit"
## [16] "Nonsense-Mediated Decay (NMD)"
## [17] "Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD) enhanced by the Exon Junction Complex (EJC)"
## [18] "Selenoamino acid metabolism"
## [19] "Eukaryotic Translation Initiation"
## [20] "Cap-dependent Translation Initiation"
## [21] "Influenza Viral RNA Transcription and Replication"
## [22] "Influenza Life Cycle"
## [23] "Regulation of expression of SLITs and ROBOs"
## [24] "Major pathway of rRNA processing in the nucleolus and cytosol"
## [25] "rRNA processing in the nucleus and cytosol"
## [26] "rRNA processing"
## [27] "Signaling by ROBO receptors"
## [28] "Negative regulators of DDX58/IFIH1 signaling"
## [29] "Infectious disease"
## [30] "Interferon gamma signaling"
## [31] "Translation"
## [32] "Metabolism of amino acids and derivatives"
## [33] "DDX58/IFIH1-mediated induction of interferon-alpha/beta"
## [34] "NF-kB activation through FADD/RIP-1 pathway mediated by caspase-8 and -10"
## [35] "TRAF3-dependent IRF activation pathway"
## [36] "PD-1 signaling"
## [37] "TRAF6 mediated NF-kB activation"
##
## $CD66nCD45p.Responder_dose2
## [1] "Interferon Signaling"
## [2] "Interferon alpha/beta signaling"
## [3] "Peptide chain elongation"
## [4] "Viral mRNA Translation"
## [5] "Eukaryotic Translation Elongation"
## [6] "Selenocysteine synthesis"
## [7] "Eukaryotic Translation Termination"
## [8] "Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD) independent of the Exon Junction Complex (EJC)"
## [9] "Formation of a pool of free 40S subunits"
## [10] "L13a-mediated translational silencing of Ceruloplasmin expression"
## [11] "SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane"
## [12] "GTP hydrolysis and joining of the 60S ribosomal subunit"
## [13] "Nonsense-Mediated Decay (NMD)"
## [14] "Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD) enhanced by the Exon Junction Complex (EJC)"
## [15] "Influenza Infection"
## [16] "Selenoamino acid metabolism"
## [17] "Eukaryotic Translation Initiation"
## [18] "Cap-dependent Translation Initiation"
## [19] "Influenza Viral RNA Transcription and Replication"
## [20] "Influenza Life Cycle"
## [21] "Regulation of expression of SLITs and ROBOs"
## [22] "Major pathway of rRNA processing in the nucleolus and cytosol"
## [23] "rRNA processing in the nucleus and cytosol"
## [24] "rRNA processing"
## [25] "Signaling by ROBO receptors"
## [26] "Metabolism of amino acids and derivatives"
## [27] "Infectious disease"
## [28] "Translation"
## [29] "Formation of the ternary complex, and subsequently, the 43S complex"
## [30] "Translation initiation complex formation"
## [31] "Ribosomal scanning and start codon recognition"
## [32] "Activation of the mRNA upon binding of the cap-binding complex and eIFs, and subsequent binding to 43S"
## [33] "Interferon gamma signaling"
## [34] "ISG15 antiviral mechanism"
## [35] "Antiviral mechanism by IFN-stimulated genes"
## [36] "Formation of Fibrin Clot (Clotting Cascade)"
## [37] "Immunoregulatory interactions between a Lymphoid and a non-Lymphoid cell"
## [38] "Intrinsic Pathway of Fibrin Clot Formation"
## [39] "Regulation of IFNA signaling"
##
## $rest.Responder_dose2
## [1] "Interferon Signaling"
## [2] "Interferon alpha/beta signaling"
## [3] "Antiviral mechanism by IFN-stimulated genes"
## [4] "ISG15 antiviral mechanism"
## [5] "Interferon gamma signaling"
## [6] "Immunoregulatory interactions between a Lymphoid and a non-Lymphoid cell"
## [7] "Antigen activates B Cell Receptor (BCR) leading to generation of second messengers"
## [8] "Adherens junctions interactions"
## [9] "Antimicrobial peptides"
## [10] "Cell-cell junction organization"
## [11] "Translocation of ZAP-70 to Immunological synapse"Discriminant score
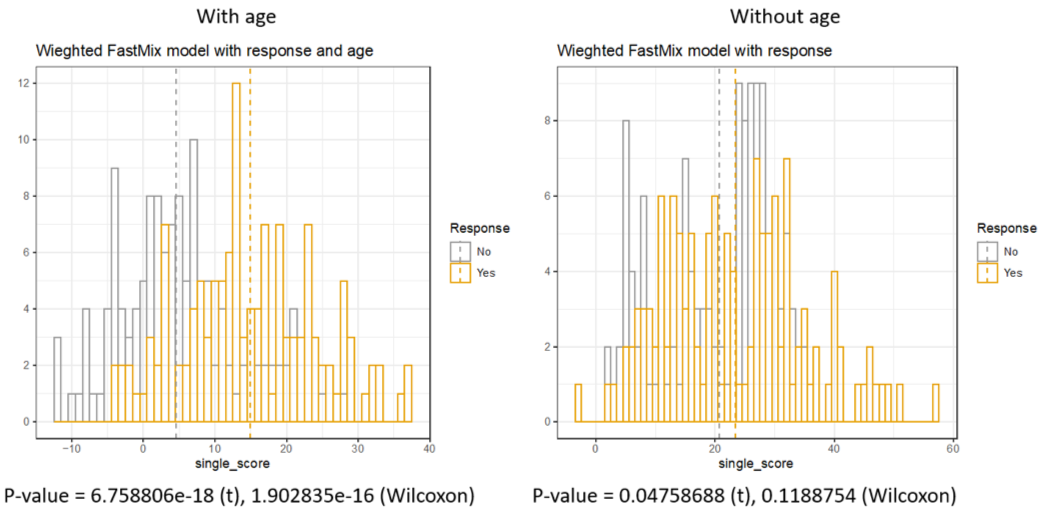
Lastly, we conducted a leave-two-out (one responder and one non-responder) cross-validation on the following two FastMix models: \[\mbox{gene expression ~ cell proportions + response after dose 2 + age,}\] \[\mbox{gene expression ~ cell proportions + response after dose 2.}\] The FastMix package also nicely provide a function score_func() that produces discriminant scores for “new” (left-out) subjects based on the the fitted (training) model.
In this analysis (figure below), we identified that age is a factor that can impact the difference between the responders and non-responders, which is consistent with existing knowledge about the efficacy of vaccines in different age groups.